The Definitive Guide for Dementia Fall Risk
The Definitive Guide for Dementia Fall Risk
Blog Article
Dementia Fall Risk Can Be Fun For Anyone
Table of ContentsWhat Does Dementia Fall Risk Mean?The 2-Minute Rule for Dementia Fall RiskSee This Report about Dementia Fall RiskThe Basic Principles Of Dementia Fall Risk
An autumn danger evaluation checks to see how likely it is that you will certainly drop. The evaluation generally includes: This consists of a series of inquiries about your total health and if you have actually had previous falls or troubles with equilibrium, standing, and/or walking.STEADI consists of screening, examining, and treatment. Interventions are referrals that may decrease your danger of dropping. STEADI includes three actions: you for your danger of dropping for your threat elements that can be boosted to try to prevent drops (for instance, balance troubles, damaged vision) to minimize your risk of dropping by using effective techniques (as an example, providing education and sources), you may be asked a number of questions including: Have you fallen in the past year? Do you feel unstable when standing or walking? Are you bothered with falling?, your service provider will certainly check your toughness, balance, and gait, utilizing the following loss assessment tools: This test checks your stride.
After that you'll take a seat once again. Your company will certainly check the length of time it takes you to do this. If it takes you 12 seconds or more, it might suggest you are at higher risk for a loss. This examination checks toughness and equilibrium. You'll being in a chair with your arms went across over your upper body.
The placements will certainly get harder as you go. Stand with your feet side-by-side. Relocate one foot halfway ahead, so the instep is touching the big toe of your other foot. Move one foot totally in front of the various other, so the toes are touching the heel of your other foot.
The smart Trick of Dementia Fall Risk That Nobody is Talking About
Most falls happen as an outcome of numerous contributing variables; for that reason, managing the danger of dropping starts with recognizing the factors that add to fall danger - Dementia Fall Risk. Several of the most relevant risk elements consist of: Background of previous fallsChronic clinical conditionsAcute illnessImpaired stride and balance, reduced extremity weaknessCognitive impairmentChanges in visionCertain risky medicines and polypharmacyEnvironmental elements can additionally boost the threat for falls, consisting of: Inadequate lightingUneven or damaged flooringWet or unsafe floorsMissing or harmed handrails and order barsDamaged or incorrectly fitted devices, such as beds, wheelchairs, or walkersImproper use assistive devicesInadequate supervision of individuals living in the NF, including those who show hostile behaviorsA successful autumn threat monitoring program calls for a detailed clinical assessment, with input from all participants of the interdisciplinary group
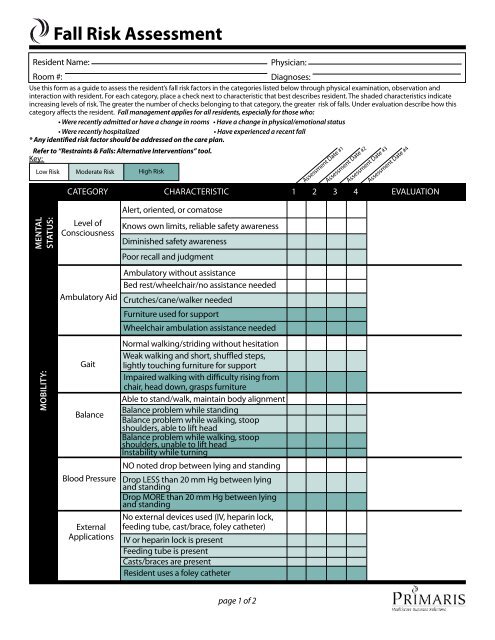
The treatment strategy need to additionally consist of treatments that are system-based, such as those that advertise a risk-free atmosphere (suitable lighting, handrails, grab bars, etc). The effectiveness of the interventions need to be reviewed periodically, and the treatment strategy revised as required to show changes in the autumn threat evaluation. Applying a loss danger administration system utilizing evidence-based finest practice can reduce the frequency of drops in the NF, while restricting the capacity for fall-related injuries.
Dementia Fall Risk - An Overview
The AGS/BGS standard advises screening all adults matured 65 years and older for fall risk each year. This screening contains asking patients whether they have actually fallen 2 or more times in the past year or looked for medical focus for a fall, or, if they have not dropped, whether they feel unsteady when strolling.
Individuals that have dropped once without injury needs to have their balance and gait reviewed; those with gait or balance problems must obtain added analysis. A history of 1 loss without additional resources injury and without stride or balance problems does not require more evaluation past continued yearly autumn threat screening. Dementia Fall Risk. A loss threat evaluation is called for as component of the Welcome to Medicare examination

The Buzz on Dementia Fall Risk
Documenting a drops background is one of the top quality signs for autumn prevention and monitoring. copyright drugs in certain are independent predictors of falls.
Postural hypotension can usually be eased by lowering the dose of blood pressurelowering drugs and/or quiting medicines that have orthostatic hypotension as an adverse effects. Use above-the-knee support pipe and copulating the head of the bed raised may likewise minimize postural reductions in high blood pressure. The recommended aspects of a fall-focused checkup are received Box 1.

A yank time greater than or equal to 12 secs suggests high autumn threat. The 30-Second Chair Stand test examines reduced extremity toughness and equilibrium. Being unable to stand up from a chair of knee height without making use of one's arms indicates boosted loss risk. The 4-Stage Balance test analyzes fixed balance by having the client stand in 4 settings, each considerably more difficult.
Report this page